Tích phân
Cách 1: Dựng hình thang
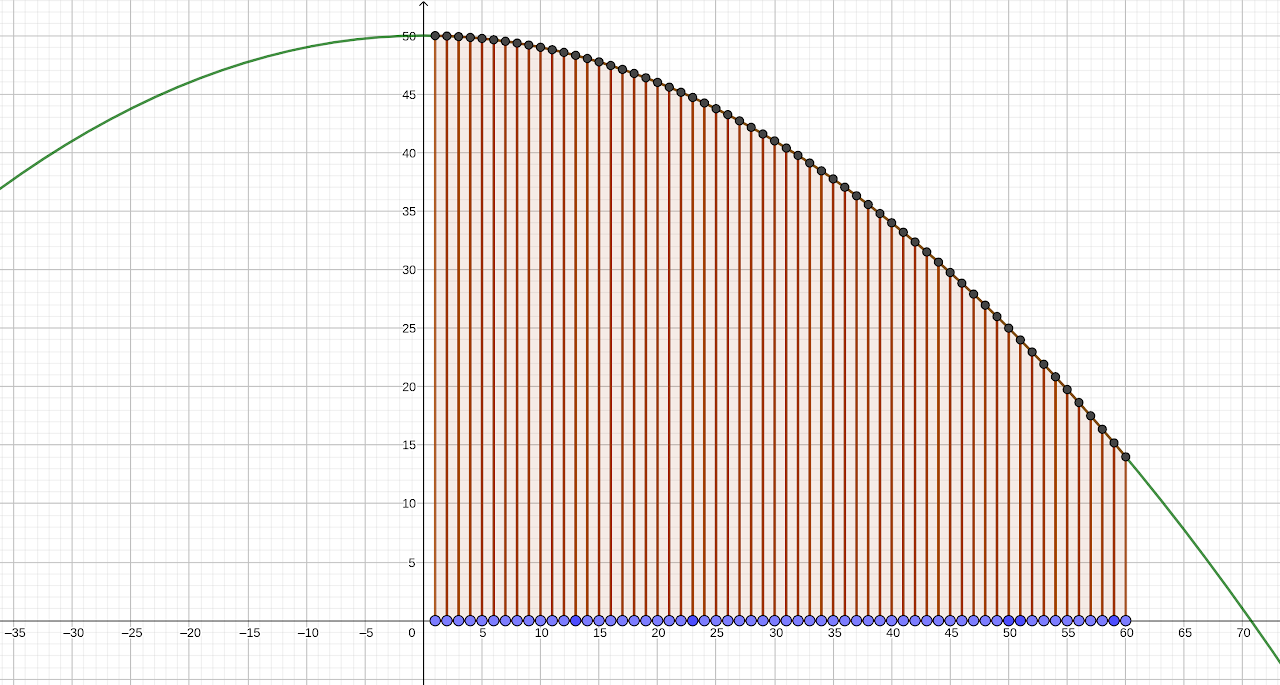
const int STEP = 1e6;
double f(double x) {
/* function here */
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1)/STEP;
double S = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < STEP; ++i) {
S += (f(x1+i*d)+f(x1+(i+1)*d))*d/2;
}
return S;
}
- Có thể gộp công thức lại như sau:
const int STEP = 1e6;
double f(double x) {
/* function here */
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1)/STEP;
double S = f(x1) + f(x2);
for (int i = 1; i < STEP; ++i) {
S += 2*f(x1+i*d);
}
return S*d/2;
}
Cách 2: Simpson’s rule ver 1
const int STEP = 1e6;
double f(double x) {
/* function here */
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1)/STEP;
double S = f(x1) + f(x2);
for (int i = 1; i < STEP; ++i) {
S += f(x1+i*d) * (i&1?4:2);
}
return S*d/3;
}
Cách 3: Simpson’s rule ver 2
const double eps = 1e-12;
double f(double x) {
/* function here */
}
double simpson(double x1, double x2) {
return (x2-x1)/6*(f(x1)+f(x2)+4*f((x1+x2)/2));
}
double integral(double x1, double x2, double ans) {
double m = (x1+x2)/2;
double lef = simpson(x1,m);
double rig = simpson(m,x2);
if (fabs(lef+rig-ans) < eps) return ans;
return integral(x1,m,lef) + integral(m,x2,rig);
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
return integral(x1,x2,simpson(x1,x2));
}
- Nhận xét: cách 1 và 2 đều có độ phức tạp là \(O(STEP*k)\) với \(k\) là độ phức tạp khi tính giá trị hàm trong khi cách 3 thì khá khó để tính độ phức tạp, tốc độ chạy thay đổi tùy đoạn \([x1,x2]\).
Tham khảo thêm
- Tích phân: https://vi.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tích_phân
- Simpson’s rule: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simpson’s_rule
- Simpson’s rule ver 1: https://cp-algorithms.com/num_methods/simpson-integration.html
- Simpson’s rule ver 2: https://discuss.codechef.com/t/a-tutorial-on-adaptive-simpsons-method/19991
- Green’s theorem: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Green’s_theorem
Bài tập
- https://codeforces.com/blog/entry/8242
- https://discuss.codechef.com/t/problems-for-adaptive-simpsons-method/20097
- Stolen: drive.google.com/file/d/13f8l02T5nfzRJ7gfX2cIZvNQqq_ZCMT_/view – Test chấm
Code giải một số bài tập
ellipse
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-12;
double a, b;
double f(double x) {
/* function here */
return b*sqrt((1-x/a)*(1+x/a));
}
double simpson(double x1, double x2) {
return (x2-x1)/6*(f(x1)+f(x2)+4*f((x1+x2)/2));
}
double integral(double x1, double x2, double ans) {
double m = (x1+x2)/2;
double lef = simpson(x1,m);
double rig = simpson(m,x2);
if (fabs(lef+rig-ans) < eps) return ans;
return integral(x1,m,lef) + integral(m,x2,rig);
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
return integral(x1,x2,simpson(x1,x2));
}
int main() {
int t; cin >> t;
cout << setprecision(3) << fixed;
while (t--) {
double x1, x2;
cin >> a >> b >> x1 >> x2;
cout << integral(x1,x2)*2 << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Enviroment Protection
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int STEP = 1e3;
const double eps = 1e-6;
double W, D, A, K;
struct Func {
int k;
vector<double> a, b;
void init(int k_) {
k = k_;
a.resize(k+1);
b.resize(k+1);
}
friend istream& operator >> (istream&is,Func&f) {
for (int i = 0; i <= f.k; ++i) {
is >> f.a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= f.k; ++i) {
is >> f.b[i];
}
return is;
}
Func operator - (double t) {
Func tmp = *this;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) {
tmp.a[i] -= t*tmp.b[i];
} return tmp;
}
double eval(double x) {
double A = 0;
double B = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) {
A += a[i]*pow(x,i);
B += b[i]*pow(x,i);
} return A/B;
}
double integralPos(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1) / STEP;
double S = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < STEP; ++i) {
double s = (eval(x1+i*d) + eval(x1+(i+1)*d)) * d / 2;
if (s > 0) S += s;
} return S;
}
} yy1, yy2;
double solve() {
double up = 0;
double down = -D;
while (fabs(up-down)>eps) {
double m = (up+down)/2;
double S = (yy1-m).integralPos(0,W)-(yy2-m).integralPos(0,W);
if (S+eps<A) up = m;
else down = m;
}
return -up;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << setprecision(5) << fixed;
while (cin >> W >> D >> A >> K) {
yy1.init(K); yy2.init(K);
cin >> yy1 >> yy2;
cout << solve() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Curvy Little Bottles
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int STEP = 1e3;
const double eps = 1e-6;
double W, D, A, K;
struct Func {
int k;
vector<double> a, b;
void init(int k_) {
k = k_;
a.resize(k+1);
b.resize(k+1);
}
friend istream& operator >> (istream&is,Func&f) {
for (int i = 0; i <= f.k; ++i) {
is >> f.a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= f.k; ++i) {
is >> f.b[i];
}
return is;
}
Func operator - (double t) {
Func tmp = *this;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) {
tmp.a[i] -= t*tmp.b[i];
} return tmp;
}
double eval(double x) {
double A = 0;
double B = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= k; ++i) {
A += a[i]*pow(x,i);
B += b[i]*pow(x,i);
} return A/B;
}
double integralPos(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1) / STEP;
double S = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < STEP; ++i) {
double s = (eval(x1+i*d) + eval(x1+(i+1)*d)) * d / 2;
if (s > 0) S += s;
} return S;
}
} yy1, yy2;
double solve() {
double up = 0;
double down = -D;
while (fabs(up-down)>eps) {
double m = (up+down)/2;
double S = (yy1-m).integralPos(0,W)-(yy2-m).integralPos(0,W);
if (S+eps<A) up = m;
else down = m;
}
return -up;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << setprecision(5) << fixed;
while (cin >> W >> D >> A >> K) {
yy1.init(K); yy2.init(K);
cin >> yy1 >> yy2;
cout << solve() << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
GM-pineapple
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-12;
const double PI = acos(-1);
int n;
double a, b;
double f(double x) {
return b*b*(1-x/a)*(1+x/a);
}
double simpson(double x1, double x2) {
return (x2-x1)/6*(f(x1)+f(x2)+4*f((x1+x2)/2));
}
double integral(double x1, double x2, double ans) {
double m = (x1+x2)/2;
double lef = simpson(x1,m);
double rig = simpson(m,x2);
if (fabs(lef+rig-ans) < eps) return ans;
return integral(x1,m,lef) + integral(m,x2,rig);
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
return integral(x1,x2,simpson(x1,x2));
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed;
cin >> b >> a >> n;
double d = a / n;
a /= 2; b /= 2;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << integral(-a+i*d,-a+(i+1)*d)*PI << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
Stolen
// public: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1yJmkstPMC-BJxrVR5vAhGQH1MB_QJ8Pq?fbclid=IwAR1DPVOCynn1ZEKZ5-2jqhvoXFF7baF7kzkskE95E5o0_F0MwnNuGJSTgD8
// link de: https://drive.google.com/file/d/13f8l02T5nfzRJ7gfX2cIZvNQqq_ZCMT_/view
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define Point Vector
#define fi first
#define se second
#define debug(x) cerr << #x << " = " << x << '\n'
using namespace std;
const double eps = 1e-6;
const double PI = acos(-1);
const int STEP = 1e6;
double cub(double x) {
return x*x*x;
}
double cubr(double x) {
if (x < 0) return -pow(-x,1.0/3);
return pow(x,1.0/3);
}
vector<double> FirstDegreeEquation(double a, double b) {
return {-b/a};
}
vector<double> QuadraticEquation(double a, double b, double c) {
double delta = b*b - 4*a*c;
if (delta < 0) return {};
if (fabs(delta) <= eps) {
return {-b/(2*a)};
}
double x1 = (-b-sqrt(delta)) / (2*a);
double x2 = (-b+sqrt(delta)) / (2*a);
return {x1,x2};
}
vector<double> CubicEquation(double a, double b, double c, double d) {
double delta = b*b - 3*a*c;
if (abs(delta) <= eps) {
double k = b*b*b - 27*a*a*d;
if (fabs(k)-1 <= eps) {
return {-b/(3*a)};
}
else {
return {(-b+cubr(k))/(3*a)};
}
}
else {
double k = (9*a*b*c - 2*b*b*b - 27*a*a*d) / (2*sqrt(cub(fabs(delta))));
if (delta > 0) {
if (fabs(k) <= 1) {
double x1 = (2*sqrt(delta)*cos(acos(k)/3) - b) / (3*a);
double x2 = (2*sqrt(delta)*cos(acos(k)/3 - 2*PI/3) - b) / (3*a);
double x3 = (2*sqrt(delta)*cos(acos(k)/3 + 2*PI/3) - b) / (3*a);
return {x1,x2,x3};
}
else {
double x = sqrt(fabs(delta))*fabs(k)/(3*a*k);
x *= cubr(fabs(k)+sqrt(k*k-1)) + cubr(fabs(k)-sqrt(k*k-1));
x -= b / (3*a);
return {x};
}
}
else {
double x = sqrt(fabs(delta))/(3*a);
x *= cubr(k+sqrt(k*k+1)) + cubr(k-sqrt(k*k+1));
x -= b / (3*a);
return {x};
}
}
}
struct Vector {
double x, y;
friend istream& operator >> (istream&is, Vector&p) {
is >> p.x >> p.y;
return is;
}
friend ostream& operator << (ostream&os, Vector p) {
os << p.x << ' ' << p.y;
return os;
}
Vector operator - (Vector a) {
return {x-a.x,y-a.y};
}
double operator % (Vector a) {
return x*a.y - a.x*y;
}
friend bool CWW(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return (b-a)%(c-b) > 0;
}
};
struct func3 {
double a, b, c, d;
friend istream& operator >> (istream&is,func3&f) {
is >> f.a >> f.b >> f.c >> f.d;
return is;
}
friend ostream& operator << (ostream&os, func3&f) {
os << f.a << ' ' << f.b << ' ' << f.c << ' ' << f.d;
return os;
}
double eval(double x) {
return a*x*x*x + b*x*x + c*x + d;
}
friend Point inter(func3 f, func3 g) {
double aa = f.a - g.a;
double bb = f.b - g.b;
double cc = f.c - g.c;
double dd = f.d - g.d;
vector<double> v;
if (aa==0) {
if (bb==0) {
v = FirstDegreeEquation(cc,dd);
}
else {
v = QuadraticEquation(bb,cc,dd);
}
}
else {
v = CubicEquation(aa,bb,cc,dd);
}
vector<Point> res;
for (double &x : v) {
res.push_back({x,f.eval(x)});
}
return res[0];
}
double integral(double x1, double x2) {
double d = (x2-x1) / STEP;
double S = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < STEP; ++i) {
S += (eval(x1+i*d)+eval(x1+(i+1)*d))*d/2;
}
return S;
}
};
func3 f[3];
vector<pair<Point,int>> v;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cin >> f[0] >> f[1] >> f[2];
Point p01 = inter(f[0],f[1]);
Point p02 = inter(f[0],f[2]);
Point p12 = inter(f[1],f[2]);
v.push_back({p01,3});
v.push_back({p02,5});
v.push_back({p12,6});
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),[&](pair<Point,int>&a,pair<Point,int>&b) {
return a.fi.x < b.fi.x;
});
cout << setprecision(6) << fixed;
if (CWW(v[0].fi,v[2].fi,v[1].fi)) {
func3 f1 = f[int(log2(v[0].se & v[1].se))];
func3 f2 = f[int(log2(v[1].se & v[2].se))];
func3 f3 = f[int(log2(v[0].se & v[2].se))];
double res = f1.integral(v[0].fi.x,v[1].fi.x) - f3.integral(v[0].fi.x,v[1].fi.x);
res += f2.integral(v[1].fi.x,v[2].fi.x) - f3.integral(v[1].fi.x,v[2].fi.x);
cout << res << '\n';
}
else {
func3 f1 = f[int(log2(v[0].se & v[2].se))];
func3 f2 = f[int(log2(v[0].se & v[1].se))];
func3 f3 = f[int(log2(v[1].se & v[2].se))];
double res = f1.integral(v[0].fi.x,v[1].fi.x) - f2.integral(v[0].fi.x,v[1].fi.x);
res += f1.integral(v[1].fi.x,v[2].fi.x) - f3.integral(v[1].fi.x,v[2].fi.x);
cout << res << '\n';
}
return 0;
}